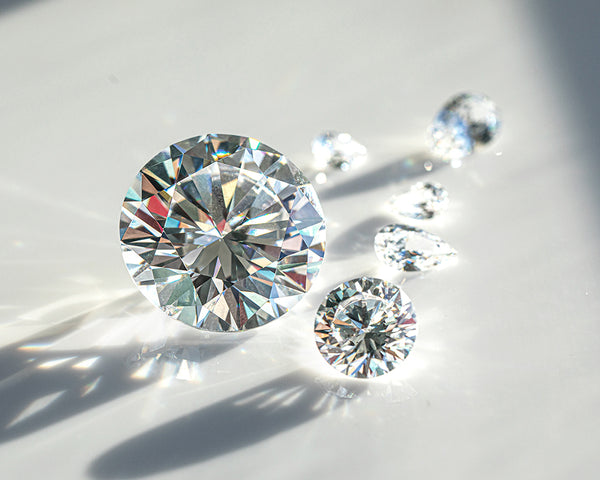
Diamond Cut
What Is Diamond Cut?
Diamond cut refers to how well a diamond’s facets interact with light. Unlike shape (round, oval, etc.), cut is about proportion, symmetry, and polish — all of which affect a diamond’s fire, brilliance, and scintillation. A masterfully cut diamond will reflect and refract light to create that sparkle we all know and love, even if it is smaller weight in carats.
Diamond Cut Grades Explained
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) assigns cut grades ranging from Excellent to Poor for round brilliant diamonds. The grades assess factors like brightness, fire, scintillation, weight ratio, symmetry, and polish. At Lucenjuri, we prioritize Excellent and Very Good cuts to ensure your lab grown diamond captures the most light.
How Diamond Cut Affects Sparkle and Brilliance
Of the 4 Cs, cut is the most important when it comes to visual beauty. A poorly cut diamond may be highly graded for clarity and color but can still appear dull and unappealing. A well-cut diamond will have ideal proportions, precise angles, and the ability for light to bounce and refract from the facets for optimal brilliance.